PEROXISOME DEFINITION
We can divide the word peroxisome into two words, ‘Peroxi’ and ‘Some’. Peroxide this word comes from Hydrogen Peroxide. Hydrogen Peroxide is a compound that is synthesized and also degraded into the peroxisome. Christian de Duve in 1965 discovered the peroxisome. Hydrogen Peroxide’s chemical formula is H2O2. The peroxisome is very simple and double membrane-bound. That means it’s got a double membrane and a tiny organelle. Sometimes, it’s called a crystalloid core. So the diameter is about 0.1 to 1.0 μm. The peroxisome is present in all eukaryotes animals.
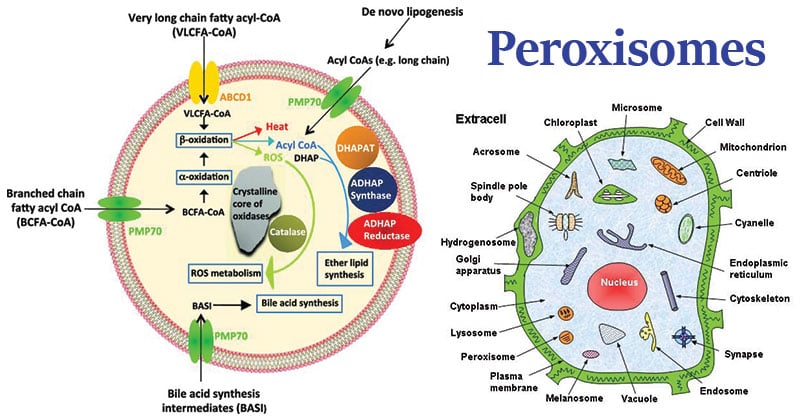
PEROXISOME FUNCTION
- The peroxisome is an important site where the catabolism of long-chain fatty acids takes place. Branching fatty acids, D amino acids, and polyamines are also catalyzed in the peroxisome.
- The reduction of reactive oxygen species occurs in the peroxisome because the peroxisome has a vital enzyme known as catalase.
- Biosynthesis of plasmalogen happens in the peroxisome, and plasma leucine is so essential for our nervous system, especially for our neurons.
- Approximately 10% of the enzymatic activity essential for the pentose phosphate pathway happens in the peroxisome. It turns out that crucial enzymes of Quinto’s phosphate pathway are present in the peroxisome.
- Scientists are still not sure, but people think that we can also synthesize isoprenoid and coalesced cholesterol inside the peroxisome because the synthesis machinery is present there.
PEROXISOME ENZYME
It has many oxidase enzymes as well. So, oxidation catalysts enzymes are the key enzymes present in the ribose in the inner peroxisomes. The enzyme oxidase would oxidize any long-chain fatty acid or D amino acid etc. The H2O2 production is not suitable for the cell. However, H2O2 is also in the reactive oxygen species. Somehow, the enzyme catalase converts H202 into a less harmful state. So catalase catalyzes the breakdown of Hydrogen Peroxide to water and oxygen. Water and oxygen none of them are detrimental to the cell. This is how our body recycles and breaks down the harmful substances inside the peroxisome.
PEROXISOME OXIDATION
The primary function of the peroxisome is to break down the oxidation of long-chain fatty acids like mitochondria. Oxidation of fatty acid also occurs in the peroxisome, but there is some basic difference between the two. In peroxisome, our body produces acetyl co A but only in a single formation. The production process of acetyl co A does not yield ATP, just like what happens in mitochondrial beta-oxidation. But this acetyl co A is an important recycled product because acetyl co A is at the centre of many catabolic and anabolic pathways. Acetyl co A is so important from ketone body production to fatty acid production, cholesterol biosynthesis, to phospholipid biosynthesis in many of these processes. That is generated inside the peroxisome, which could be used by this cell to produce several other metabolic products. In that respect, peroxisomes function is pretty important.

PEROXISOME PLASMALOGEN SYNTHESIS
The peroxisome has all the important enzymes which are important for the initial step of production of the plasmalogen. So dihydroxyacetone phosphate or DHAP produces plasmalogen in a few sequential steps. It forms one alkyl g3p, which gets transported into the endoplasmic reticulum. The successive steps happen in the endoplasmic reticulum. So both the peroxisome and the endoplasmic reticulum play an important part in the synthesis of plasmalogens which is so important for the nervous system itself. Especially for its detoxification and recycling function, peroxisome is important for the liver and kidney because most xenobiotic and harmful compounds are detoxified in the liver and kidneys, So peroxisomes in liver cells and kidney cells are very important.

PEROXISOME MECHANISM
The peroxisome is encoded by the genes inside the nucleus, which are transcribed to produce the mRNA of these enzymes. This mRNA goes out and on the ribosome present on the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. The protein is translated and folded inside the endoplasmic reticulum. Now once it is in the endoplasmic reticulum, it is then transported to the peroxisome.
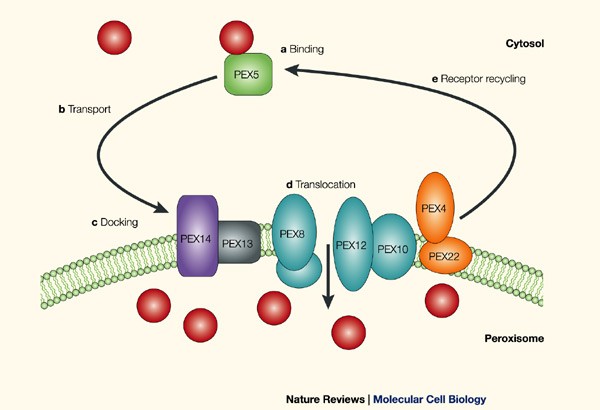
PROTEIN TRANSPORT TO PEROXISOME
Any protein or enzyme transported to the peroxisome has an important peroxisomal target sequence(PTS). This peroxisomal target sequence helps to target the protein towards the peroxisome. There is an important translocon channel on the peroxisome membrane known as spec 17, which helps the peroxisomal target sequence containing protein get inside the peroxisome. This peroxisome targeting sequence would eventually blind to the peroxisome target sequence receptor(PTSR). This peroxisome target sequence receptor interacts with the pic 17 channel and allows this enzyme. We need this enzyme to deliver into the peroxisome to get inside the peroxisome.Read Also: Glycerol: Properties, Formula & Uses
PEROXISOMAL OXIDASE
Peroxisomal oxidase is helping to convert the launcher fatty acid to acetyl co A itself. These oxidase enzymes need to be delivered to the peroxisome in the first place, but the ADL gene codes for one particular translocon protein. This translocon protein helps the oxidase enzymes to get inside the peroxisome. In the mutated ABL gene, the mutated gene can no longer produce the translocon protein. As a result, the important oxidase enzyme can not enter the peroxisome. The oxidation of long-chain fatty acid does not occur in disease situations, and the symptoms are detrimental.
PEROXISOME STRUCTURE
- It’s very simple and has a double membrane-bound small organelle.
- Diameter 0.1 to 1.0 μm.
- Present in all eukaryotes.
- It contains a dense, crystalline core of oxidative enzymes (more than 50 enzymes).
- Lack of DNA and ribosomes – thus, nuclear genes encode and synthesize all protein on Ribosomes present in the cytosol or endoplasmic reticulum.
- It can divide itself and transport post-translational proteins. They might have endosymbiotic origins.
- Synthesize luciferase – enzyme that emits light.

PEROXISOME LOCATION
Peroxisomes are present in all eukaryotic cells. We can find it in yeast, protozoa, and more cell types of higher plants.
PEROXISOME FUNCTION IN PLANT CELL
Plants cells have peroxisome as well. Peroxisome converts reactive O2 species into other fragments that are non-toxic to the cell. They perform several particular functions in plants. Peroxisomes in leaf cells, for example, play a critical role in photorespiration. Peroxisomes are very important in seed growth and germination.
PEROXISOME VS LYSOSOME
Lysosomes are coming from the Golgi apparatus. When the signal comes to the rough endoplasmic reticulum, they form some proteins which travel towards the mitochondria. They become vesicles that contain some enzymes or proteins. Lysosomes may be of two types, the primary lysosomes or the secondary lysosomes. If a vesicle is coming from the Golgi apparatus, it has not been combined with any vesicle. But peroxisomes are coming from the endoplasmic reticulum. Their functions are also a bit different. The enzymes that are present in the peroxisomes are oxidizing. Oxidize different substances rather than hydrolases.
Some Frequently Asked Questions
What is the function of the peroxisome?
The peroxisome is an important site where the catabolism of long-chain fatty acids reduces reactive oxygen species.
Why is the peroxisome important?
The peroxisome is so important for our human body. Because it converts H2O2 into water and oxygen and protects the cell, also, it detoxifies alcohol in liver cells.
What are the three functions of peroxisomes?
Peroxisomes involve the catabolism of long-chain fatty acids, reduction of reactive oxygen species, plasmalogen biosynthesis, and enzymatic activity.
What is the difference between a lysosome and a peroxisome?
The lysosome is a collapsed biological polymer like proteins and polysaccharides. Other hands, a peroxisome is a collapsed hydrogen peroxide.
Do peroxisomes detoxify drugs?
Yes, peroxisomes detoxify alcohol in liver cells.
Who discovered peroxisomes?
Christian de Duve in 1965 discovered the peroxisome.
How did peroxisomes get named?
Peroxisomes this name comes from hydrogen peroxide.