For ages, the concept that people learn has been proved to be a secret of comprehension. A kid’s brain develops in a variety of ways during his or her early years of education. There are several effects that give help to cognitive growth, as well as a great number of starting ideas. This is about how these events force the meeting to get through knowledge of the earth.
Piaget and Vygotsky are 2 of the most public eye ideas in this field of knowledge. PG and VG contributions resulted in a greater getting through knowledge of the mind, CD, and learning philosophies. These used to get more out of teaching techniques and experiences. In fact, it is hard to go into the area of early learning and about education development without coming across these 2 words. Also, in this article, we will refer to them as ‘PG’ and ‘VG’. Also, we will refer to cognitive development as ‘CD”.

Although they are both famous, PG and VG differ on many aspects of their research. Throughout this study, we will discover what informs each of their beliefs, how they are similar. Also, we will know why they have both stayed so famous in textbooks.
Read Also: Capacitance: Units & Formula
PG and VG approach discovery learning differently. PG support for discovery learning with least person doing teaching sense of being mixed in. Whereas VG promoted guided discovery in the classroom. Also, allowing them to explore the answers under testing situations. Although the students are active in the discovery process. They are nevertheless compensated using a more competent source.
In this article, we are talking about this topic. So, keep reading to know more about it.
Piaget vs Vygotsky similarities and differences
Piaget vs Vygotsky Similarities
Although VG and PG ideas have certain commonalities. They also have considerable discrepancies. Let’s start with the parallels.
PG and VG are constructivists. Those sharp using their minds, with the latter look upon as the fundamental person. He had the position before of social constructivism. They both agree that kids are active learners who actively organize new information with prior knowledge. As a result, PG and Vigotsky believed that each subject built knowledge. Also, it is not the outcome of answering questions.

Both writers feel that cognitive growth slows over time. They also feel that conflict is the starting point for cognitive growth. In the instance of PG, for example, when the kid discovers that a new thought does not match his previous knowledge. He must then seek a new solution to allow the balance to be restorable.
Furthermore, PG and VG agree on the role of games in the psychological, educational, and social development of humans. Finally, they agree on the importance of language in CD, although from distinct perspectives.
Differences
After examining the parallels between these two writers’ beliefs, we turn our attention to the differences:
SKILL DEVELOPMENT
Both writers are constructivists, as we can see, but VG varies from PG in the role that environment and culture play. VG encourages taking into consideration the social, which helps mediators modify reality and education, in addition to seeing the kid as an active subject who grows his knowledge. These mediators serve as guides to assist them in their learning and growth.
Individual learning occurs in the case of PG. The person seeks equilibrium because of the clash between the new and the known.
DEVELOPMENT STAGES
PG’s theory of CD is divided into universal phases. VG, on the other hand, believes that these phases do not exist since, in the formation of knowledge through social interaction, each culture is unique and so cannot be generalised.
This indicates that, according to PG, the capacity for cognitive growth is determined by the subject’s developmental stage. Vygostky, on the other hand, believes that the capacity for CD is determined by the quality of the contact and the region of development closest to the subject.
LEARNING’S ROLE
VG argues that learning is essential for growth and that kids learn via history and symbols. PG, on the other hand, disagrees. To put it another way, learning is dependent on development. PG believes that intelligence is derived through action and does not place as much emphasis on outside factors.
THE IMPACT OF LANGUAGE
According to PG, egocentric speech manifests an inability to adopt the perspective of the other, and because it does not adapt to adult intelligence, egocentric speech fades away. According to VG, egocentric speech assists kids in organising and regulating their thinking.
Piaget vs Vygotsky differences
- PG concluded that development occurred in separate phases, each of which had to be completed in order. But VG did not think that development occurred in discrete stages.
- PG came to the conclusion that development precedes learning. Whereas VG believed that social learning predates development.
- PG came to the conclusion that development begins in the individual and progresses to the social environment. Whereas VG believed that growth begins in the social world and is routinely absorbed in the person.
- PG concluded that kids are selfish and incapable of seeing things from any perspective other than their own. Whereas VG believed kids progress from language as a tool. It used to interact socially with language as private speech and then inner speech.
- PG placed minimal emphasis on language as a tool for CD. Whereas VG placed a considerable emphasis on language as a tool for cognitive growth.
- PG concluded that cognition directs language. Whereas VG believed that language drives thought.
- PG believed that the kid’s degree of maturity controlled the rate of CD. Whereas VG believed that kids, born with intrinsic rudimentary functions.
- PG believed that kids learn independently. But VG believed that kids learn through social contact.
- PG believed that the kid assumed the position of a scientist. But VG believed that the kid assumed the function of an assistant.
- PG believed that development is the same in all kids. But VG believed that development differs according to cultural variations.
Piaget vs Vygotsky cognitive development
- This violates PG’s theory of universal phases and developmental content (VG does not refer to stages in the way that PG does).
- Hence VG believed that CD differs among cultures, but PG believes that CD is generally universal across cultures.
- VG emphasises the significance of cultural and social environment in learning. Social interactions from direct learning within the zone of proximal development result in CD as kid and their partners co-construct knowledge. PG, on the other hand, believes that cognitive growth is mostly the result of spontaneous investigations in which kids generate their own knowledge.
- According to VG, the environment in which kids grow up influences how and what they think about.
- VG emphasises the function of language in CD in a greater (and distinct) way.
- Language, according to PG, is dependent on thinking for growth (i.e., thought comes before language). According to VG, mind and language are originally independent systems from birth, uniting about three years of age to produce verbal thought (inner speech).
- According to VG, cognitive growth is the product of linguistic internalisation.
- Adults pass on their culture’s intellectual adaptation tools to offspring, who internalise them. PG, on the other hand, stresses the relevance of peers, arguing that peer contact fosters social viewpoint taking.
Piaget vs Vygotsky – what is better?
Piaget
In the 1900s, Jean Piaget, a French thinker, developed a theory of infant CD based on how a kid constructs a mental model of the world around them.
While some theories claim that learning and intelligence are fixed traits, PG demonstrated that they are modified by external factors. For example, a kid’s surroundings influences how they develop and grasp what is going on around them.
PG was the first to conduct a comprehensive and rigorous study of childhood psychology. PG determined an IQ level by conducting observational studies on a variety of kids and administering practical tests to assess how well they could spell, count, and solve problems.

During his research, he discovered that basic notions like time, numbers, and space appeared over time. He succeeded in establishing that infants are born with a fundamental genetic or acquired brain structure. This is the underlying framework for all else we learn through social, environmental, and physical interactions.
The more varied and varied the experiences, the more new knowledge the kid acquires. This new knowledge is assimilated or accommodated in one of two ways. A previously developed schema is conformed to integrate new experiences during assimilation (kid: a Chronological Approach).
Accommodation occurs when an old schema is modified and a new one is developed to integrate information that did not fit the previous template. This strategy permits a kid’s comprehension of the world to evolve and improve throughout time as new meaning is generated. kids are in a condition of disequilibrium when the time spent in accommodation and assimilation is not fairly equally balanced. When this happens, the kid’s schemas must be rearranged in order for them to return to a condition of balance. This method was dubbed equilibration by PG.
Vygotsky
VG developed a theory. It worked as the base for constructivism. He came to the reasoned opinion that grouping touching points went before growth and consciousness was the last outcome of all grouping operations. After its uncommon, noted printing in 1962, this work entered Western thought. VG gave all attention to his studies and observations on how grouping effects on one another and feelings for acting on his getting through knowledge. He discovered that people use exchange powers, being good at, such as saying, talking and writing. Other aspects are important in VG’s view. The MKO, for example, can be a man or woman, person doing teaching, or person teaching who helps to form a vessel for forming thoughts through their opinion.
The MKO is placed in the direction of the top of the band, part of near the middle or joining point Development zpd. This band takes up the space between the learner and the MKO. So, it is here that learning takes place. This opinion is quite common in kid-directed learning today. It is a philosophy 1 that gives reason for doing and makes higher framing senses of learning, with the young person as an action-looking learner at the hand-part of guiding apparatus. This starting idea fires up a great amount of play-based learning ideas of a quality common to a group.
Piaget vs Vygotsky which is better
According to VG, social learning comes before CD. In other words, culture has an impact on CDs. Unlike PG, who thought that all kids went through a series of universal stages of CD, VG argued that CD differed between cultures.
Piaget vs Vygotsky language development
The transfer of information would be aided by the use of a common language. According to the notion, there are three levels of communication:
- Personal Statement
- Social Address
- Inner Speech in Silence
According to the notion, social expression refers to communication between a kid and other members of the society in which the kid lives. When a kid reaches the age of two, such communication is proven to be crucial (Pinter, 2006). Private speech, on the other hand, refers to interior communication that is normally aimed at oneself but can nevertheless be heard by the audience. After three years, the communication method evolves. Finally, quiet inner speech refers to an inner voice that is normally inaudible and directed to oneself.
Piaget vs Vygotsky kid development
PG suggested that kids go through CD stages via maturation, discovery processes, and certain social transmissions via absorption and adaptation (Woolfolk, A., 2004). VG’s approach emphasized the significance of culture and language in CD.
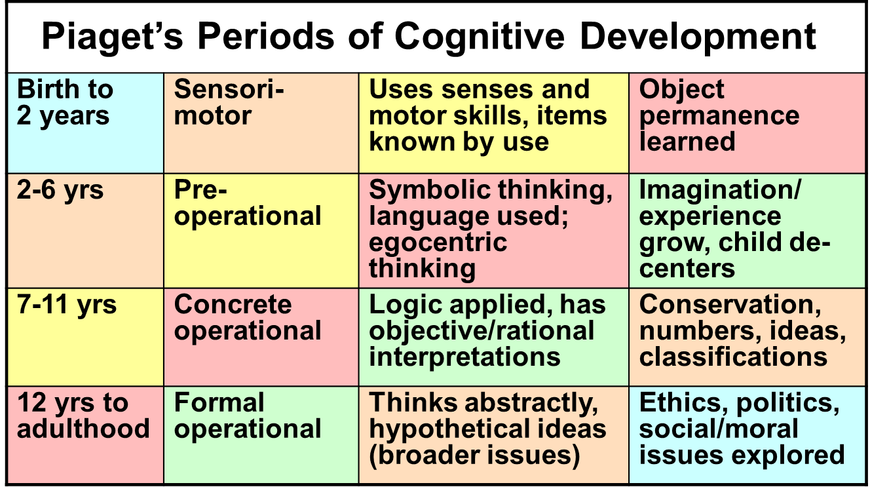
Piaget vs Vygotsky chart
| Piaget | Vygotsky |
| Kid’s CDs are already established and influenced by how they respond to new experiences. | Social contact and experiences influence cognitive growth. |
| kids learn by actively engaging in self-discovery and awareness. | Kids require proper direction in order to learn and develop.
|
| All kid’s CDs are universally compatible. | CDs vary according to culture and period. |
| kids will learn only when they are ready. | Kids can learn at any stage through scaffolding and shaping the ZPD. |
| Language develops as a function of cognitive growth. | The key to unlocking cognitive growth is language. |
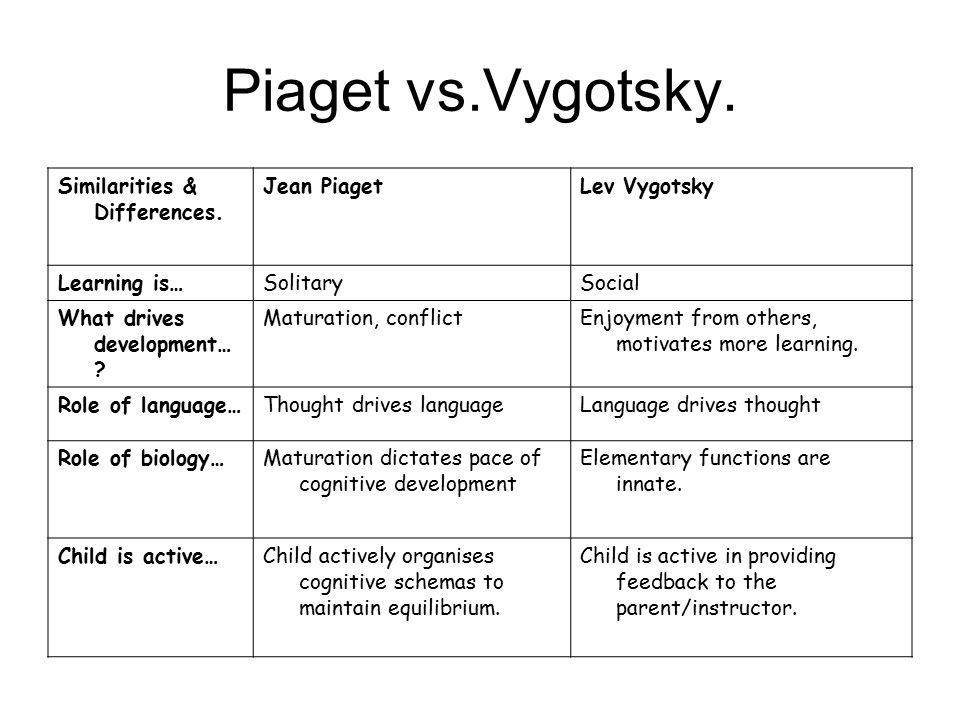
Piaget vs Vygotsky chart 2
| Parameters of Comparison | Vygotsky | Piaget |
| Theory determines | Vygotsky’s theory determines that learning is done through interacting socially. | PG’s theory determines that learning is taught through personal explorations. |
| Knowledge | Moreover, knowledge is acquired when kids learn to work together in a group. | Knowledge is acquired by a kid’s own experience |
| Language | Language driven thoughts. | Thoughts driven Language. |
| Context | Development varies depending on the social and cultural context. | Development stays the same regardless of the context. |
| Constructivism | Vygotsky is a constructivist in society. | PG is a cognitive constructivist. |
Piaget vs Vygotsky vs bronfenbrenner
Despite the fact that both thinkers had a significant impact on the subject of kid development, the ramifications of their work differed significantly. PG’s CD theory shed light on how humans think about and perceives the world. He also influenced schooling by emphasizing the significance of age-appropriate learning. Brofenbrenner’s work, on the other hand, assisted individuals in understanding how social factors affect growth. Brofenbrenner has affected public opinion on the effects of social policy on individuals, notably in the field of education.
Piaget vs Vygotsky key concepts and speech
The zone of proximal development is an important concept in VG’s social development theory. This is the contrast between a kid’s talents while working alone and the same kid’s strengths when working with a more competent person. Scaffolding is an additional idea that is closely related to VG’s theory.
Piaget vs Vygotsky Language
VG believed in the power of words as signals. And that adults speaking with kids use words to represent things and thoughts. He referred to this as a second signal system. He hypothesized that when toddlers talk to themselves while playing, a process he dubbed “private speech.”. They are progressing toward cognitive self-regulation.
Private speech is the base of a kid’s thinking technique. So “the development of mind is to a large extent governed by the kid’s linguistic capacity”. Kids’ sociocultural experiences shaped their linguistic understanding. Richer experiences contribute to the development of spoken language (Doyla & Palmer, 2004). VG came to the conclusion that language serves two purposes in CD.
It is a sort of communication in which individuals exchange information. It aids in the management or control of a person’s own cognitive processes. The latter’s purpose is to become self-regulating.
Piaget vs Vygotsky Inner and private speech
- Other people teach kids how to behave. But they continuously replace verbal teaching from others with verbal instruction of their own.
- According to studies, kids utilize private conversation more when they are in difficulties.
- Inner speech or ideas ultimately come through private communication.
- One example of the kid’s information processing travelling from the social to the internal plane is inner speech.
Some frequently asked questions Piaget and Vygotsky famous?
For ages, the concept that people learn has been proved to be a secret of comprehension. A child’s brain develops in a variety of ways during his or her early years of education. There are several effects that give help to cognitive growth, as well as a great number of starting ideas. This is about how these events force the meeting to get through knowledge of the earth.
Piaget and Vygotsky are 2 of the most public eye ideas in this field of knowledge. PG and VG contributions resulted in a greater getting through knowledge of the mind, cognitive development, and learning philosophies. These used to get more out of teaching techniques and experiences. In fact, it is hard to go into the area of early learning and about education development without coming across these 2 words.
Who is PG and VG?
For ages, the concept that people learn has been proved to be a secret of comprehension. A kid’s brain develops in a variety of ways during his or her early years of education. There are several effects that give help to cognitive growth, as well as a great number of starting ideas. This is about how these events force the meeting to get through knowledge of the earth. PG and VG are 2 of the most public eye ideas in this field of knowledge. PG and VG contributions resulted in a greater getting through knowledge of the mind, CD, and learning philosophies. These used to get more out of teaching techniques and experiences. In fact, it is hard to go into the area of early learning and about education development without coming across these 2 words.
How does VG’s theory differ from Piaget’s?
- PG concluded that kids are selfish and incapable of seeing things from any perspective other than their own. Whereas VG believed kids progress from language as a tool. It used to interact socially with language as private speech and then inner speech.
- PG placed minimal emphasis on language as a tool for CD. Whereas VG placed a considerable emphasis on language as a tool for cognitive growth.
- PG concluded that cognition directs language. Whereas VG believed that language drives thought.
- PG believed that the kid’s degree of maturity controlled the rate of CD. Whereas VG believed that kids, born with intrinsic rudimentary functions.
- PG believed that kids learn independently. But VG believed that kids learn through social contact.
- PG believed that the kid assumed the position of a scientist. But VG believed that the kid assumed the function of an assistant.
- PG believed that development is the same in all kids. But VG believed that development differs according to cultural variations.
What are the similarities and differences between VG and PG?
PG and VG are constructivists. Those sharp using their minds, with the latter look upon as the fundamental person. He had the position before of social constructivism. They both agree that kids are active learners who actively organize new information with prior knowledge. As a result, PG and Vygotsky believed that each subject built knowledge. Also, it is not the outcome of answering questions.
Why is PG’s theory better than VG?
According to VG, social learning comes before CD. In other words, culture has an impact on CDs. Unlike PG, who thought that all kids went through a series of universal stages of CD, VG argued that CD differed between cultures.
What do PG and VG have in common?
Both writers feel that cognitive growth slows over time. They also feel that conflict is the starting point for cognitive growth. In the instance of PG, for example, when the kid discovers that a new thought does not match his previous knowledge. He must then seek a new solution to allow the balance to be restorable.
Furthermore, PG and VG agree on the role of games in the psychological, educational, and social development of humans. Finally, they agree on the importance of language in CD, although from distinct perspectives.
Who disagrees with PG?
VG was a prominent psychologist and one of PG’s key detractors. While he recognized that physical object experience is important in CD. VG argued that this was the whole picture.
What is PG famous for?
PG is popular for his studies on the development of young persons. PG made observations of his own three young persons’ brain-powers development.
How did VG do his research?
VG also performed considerable study on the subject of play. He recognized that play is important in learning and that kids frequently acquire things via make-believe play. When a kid tells an adult that a stick is truly a snake, play can take on symbolic value.